mirror of
https://github.com/aantron/dream.git
synced 2025-12-31 00:03:52 -05:00
k-websocket
In this example, the client connects to the server by a
WebSocket. They then follow a
silly protocol: if the client sends "Hello?", the server responds with
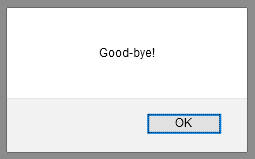
"Good-bye!". The client displays the message in an alert box:
let home =
<html>
<body>
<script>
var socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/websocket");
socket.onopen = function () {
socket.send("Hello?");
};
socket.onmessage = function (e) {
alert(e.data);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
let () =
Dream.run
@@ Dream.logger
@@ Dream.router [
Dream.get "/"
(fun _ ->
Dream.respond home);
Dream.get "/websocket"
(fun _ ->
Dream.websocket (fun websocket ->
match%lwt Dream.receive websocket with
| Some "Hello?" ->
let%lwt () = Dream.send "Good-bye!" websocket in
Dream.close_websocket websocket
| _ ->
Dream.close_websocket websocket));
]
@@ Dream.not_found
$ dune exec --root . ./websocket.exeVisit http://localhost:8080 to get the whole exchange started!
See WebSockets in the API docs.
Next steps: